Search by topic:
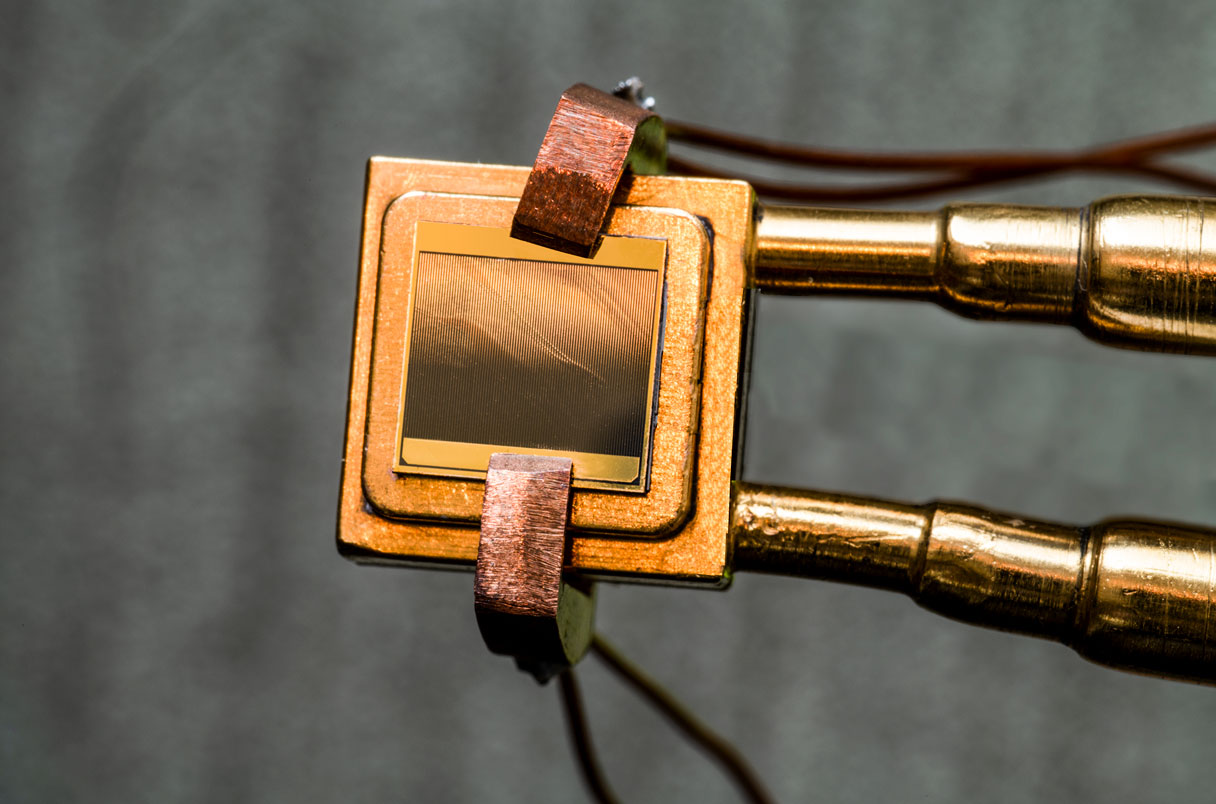
Steam turbines have to date been the most traditional way to covert heat into electricity. Steam turbines are able to convert between 35-60% of the heat into electricity. However, scientists have kept investigating alternative ways to turn heat into electricity. Thermophotovoltaic cells (TPV) were initially promising, but only ever achieved efficiency rates of 20-32%. By increasing both the temperature of the heat emitter & the absorption properties of the TVC (visible, ultraviolet & infrared) engineers at MIT have achieved efficiency rates of 40%, with a clear idea of how to reach 50%.