Search by topic:
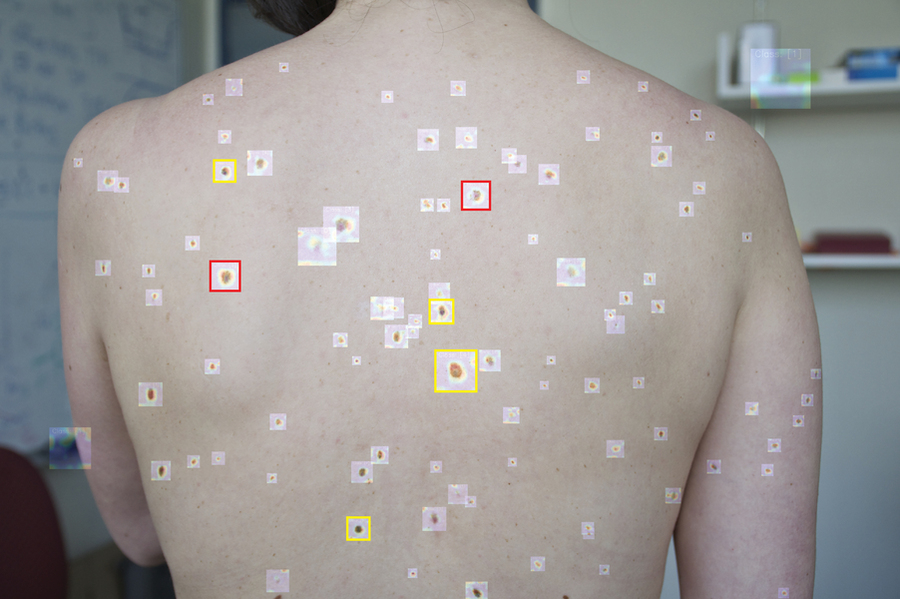
How it works: A wide-field image, acquired with a smartphone camera, shows large skin sections from a patient in a primary-care setting. An automated system detects, extracts, and analyzes all pigmented skin lesions observable in the wide-field image.
A pre-trained deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) determines the suspiciousness of individual pigmented lesions and marks them (yellow = consider further inspection, red = requires further inspection or referral to dermatologist).
Extracted features are used to further assess pigmented lesions and to display results in a heatmap format.
https://news.mit.edu/2021/artificial-intelligence-tool-can-help-detect-melanoma-0402